Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles
유전자 세트 풍부 분석: 게놈 전체 발현 프로필을 해석하기 위한 지식 기반 접근 방식
https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.0506580102
Abstract

•In a typical experiment, mRNA expression profiles are generated for thousands of genes from a collection of samples belonging to one of two classes, for example, tumors that are sensitive vs. resistant to a drug. The genes can be ordered in a ranked list L, according to their differential expression between the classes. The challenge is to extract meaning from this list.
•The goal of Gene Set Enrichment Analysis(GSEA) is to determine whether members of a gene set S tend to occur toward the top (or bottom) of the list L, in which case the gene set is correlated with the phenotypic class distinction.
DEGs에 따라 ranked list L 생성.
Methods

•Step 1: Calculation of an Enrichment Score.
•The score is calculated by walking down the list L, increasing a running-sum statistic when we encounter a gene in S and decreasing it when we encounter genes not in S.
목록 L을 따라 걸으며 S 에서 유전자를 만나면 누적 합계 통계량을 증가시키고 S 에 없는 유전자를 만나면 누적 합계 통계량을 감소시켜 계산
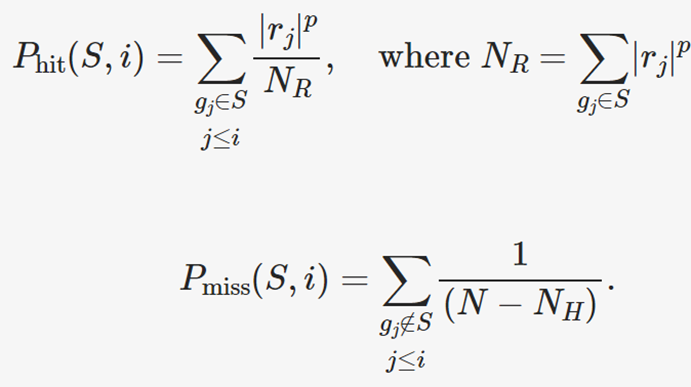
i에 대해 Phit – Pmiss 계산.
i가 S에 포함되면, Phit 상승으로, i-1일 때의 계산값보다 상승.
i가 S에 포함 안 되면, Pmiss 상승으로, i-1일 때의 계산값보다 하락.
•Step 2: Estimation of Significance Level of ES.
1. Randomly assign the original phenotype labels to samples, reorder genes, and re-compute ES(S).
=> Ranked Gene List 가 다시 형성
+) The permutation of class labels preserves gene-gene correlations
중요한 점은 클래스 라벨의 순열은 유전자-유전자 상관관계를 보존하고, 따라서 유전자를 순열하여 얻을 수 있는 것보다 생물학적으로 더 합리적인 유의성 평가를 제공한다는 것입니다.
=> 라벨을 섞는 경우 : 유전자 간 상호작용(상관성)은 그대로 유지됩니다. 이는 실제 실험 데이터의 구조를 유지한 상태에서 phenotype과의 관계가 우연히 발생한 것인지 평가할 수 있습니다.
유전자를 섞는 경우: 유전자 간 상호작용이 손실되므로, 유전자가 서로 독립적이라고 가정하게 되며, 실제 생물학적 상관관계를 반영하지 못하는 결과를 초래할 수 있습니다.
2. Repeat step 1 for 1,000 permutations, and create a histogram of the corresponding enrichment scores ESNULL.
=> 새로운 **Enrichment Score(ES)**가 계산
3. Estimate nominal P value for S from ESNULL by using the positive or negative portion of the distribution corresponding to the sign of the observed ES(S).
Observed ES(S)가 우연히 발생할 가능성을 추정.
=> 관찰된 ES가 null distribution에서 얼마나 극단적인지 평가하여 P-value를 계산합니다. 관찰된 ES보다 큰(혹은 작은) null ES의 비율이 P-value가 됩니다.
=> 이 값이 낮을수록 결과가 통계적으로 유의미하다는 뜻입니다.
•Step 3: Adjustment for Multiple Hypothesis Testing.
1.Determine ES(S) for each gene set in the collection or database.
2.For each S and 1000 fixed permutations π of the phenotype labels, reorder the genes in L and determine ES(S, π).
3.Adjust for variation in gene set size. Yield the normalized scores NES(S, π) and NES(S).

4.Compute FDR. Control the ratio of false positives.
이 과정은 GSEA에서 유전자 세트의 중요성을 평가하는 절차입니다. ES(S)는 유전자 세트가 특정 phenotype과 얼마나 연관되어 있는지를 측정합니다. 여러 permutation을 통해 무작위 데이터를 생성하고, 이를 기반으로 유전자 세트 크기 차이를 보정한 후 정규화된 NES를 계산합니다. 마지막으로, 잘못된 양성 결과의 비율을 제어하기 위해 FDR(False Discovery Rate)을 계산하여 결과의 신뢰성을 높입니다.
Example
The distribution of three gene sets, from the C2 functional collection, in the list of genes in the male/female lymphoblastoid cell line example ranked by their correlation with gender:
"성별"과의 상관관계에 따라 순위를 매김.

•S1, a set of chromosome X inactivation genes; ⇒ S1 is significantly enriched in females as expected.
chromosome X는 성별과 관련있기에, Enrichment Score가 높게 나타남. chromosome X는 여성과 관련있기에, 여성과 관련된 앞쪽에서 나타남.
•S2, a pathway describing vitamin c import into neurons; ⇒ S2 is randomly distributed and scores poorly.
비타민 C는 '성별'과는 아무런 관련이 없기에, 랜덤하게 나타남. 그래서 점수도 좋지 않음.
•S3, related to chemokine receptors expressed by T helper cells. ⇒ S3 is not enriched at the top of the list but is nonrandom, so it scores well.
중간으로 갈 수록 상승하기에, 앞쪽(top)에 몰려있지는 않다. 중간에 몰려 있기에, 랜덤하다고 볼 수는 없다. 그래서 중간 부분에서는 상승하여, score가 높다.
'AI, 논문, 데이터 분석' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Cell Ranger 설치 및 실행 (2) | 2024.11.07 |
|---|---|
| SRA Toolkit 사용해서 데이터 받기 (3) | 2024.11.06 |
| Gene Ontology (GO) Enrichment analysis 개념 정리 (1) | 2024.10.10 |
| Pathway Enrichment analysis 개념 정리 (0) | 2024.10.10 |
| [MAST, limma, DESeq2] 공통 DEGs 분석 (0) | 2024.09.19 |


